Master Snowflake Cost Monitoring in Radar
Oct 24, 2024
·
5
min read
Introduction
Snowflake's consumption-based pricing model offers flexibility and scalability, but without proper visibility, costs can spiral out of control. Analytics teams often struggle to pinpoint where their warehouse spending goes—long-running queries, oversized warehouses, and unoptimized dbt projects can drain budgets without anyone noticing until the bill arrives.
Paradime's Radar dashboard solves this challenge by providing comprehensive, real-time insights into your Snowflake costs. This guide walks you through how to leverage Radar's cost monitoring features to track daily warehouse spend, analyze query costs by user and role, identify expensive timeout queries, and optimize dbt project operations. By the end, you'll have actionable strategies to reduce warehouse spending by 20% or more while maintaining performance.
Why Snowflake Cost Monitoring Matters
Snowflake's pay-per-use model means every query executed and every second a warehouse runs directly impacts your bottom line. Without monitoring tools, teams operate blind—unable to see which users drive costs, which queries run inefficiently, or when warehouses remain active unnecessarily.
Common cost drivers include long-running analytical queries that consume credits for hours, warehouses sized larger than needed for their workloads, timeout queries that fail after burning through resources, and dbt projects with inefficient models running on expensive warehouses. These issues compound over time, turning manageable expenses into budget-busting problems.
The impact extends beyond finances. Uncontrolled costs affect team productivity as analysts second-guess every query, delay projects due to budget constraints, and spend time firefighting cost overruns instead of delivering insights. Effective cost monitoring transforms this reactive approach into proactive optimization.
Getting Started with Radar's Cost Monitoring Dashboard
Before accessing Radar's cost monitoring capabilities, complete the Cost Management setup in the Radar Get Started guide and connect your Snowflake account. This one-time configuration enables Radar to pull warehouse usage data and query metadata.
Once configured, the Snowflake Cost Monitoring interface provides a comprehensive overview of your spending patterns. The dashboard layout presents key metrics at a glance—total warehouse spend, cost trends over time, and breakdowns by user, role, and warehouse.
Two essential filters sit at the top: date range selection and warehouse filtering. The date range lets you analyze specific periods—yesterday's spike, last week's trends, or month-over-month comparisons. The warehouse filter focuses your analysis on specific warehouses, helping you drill into problem areas. The dashboard automatically updates as you adjust these filters, making it easy to explore different perspectives on your cost data.
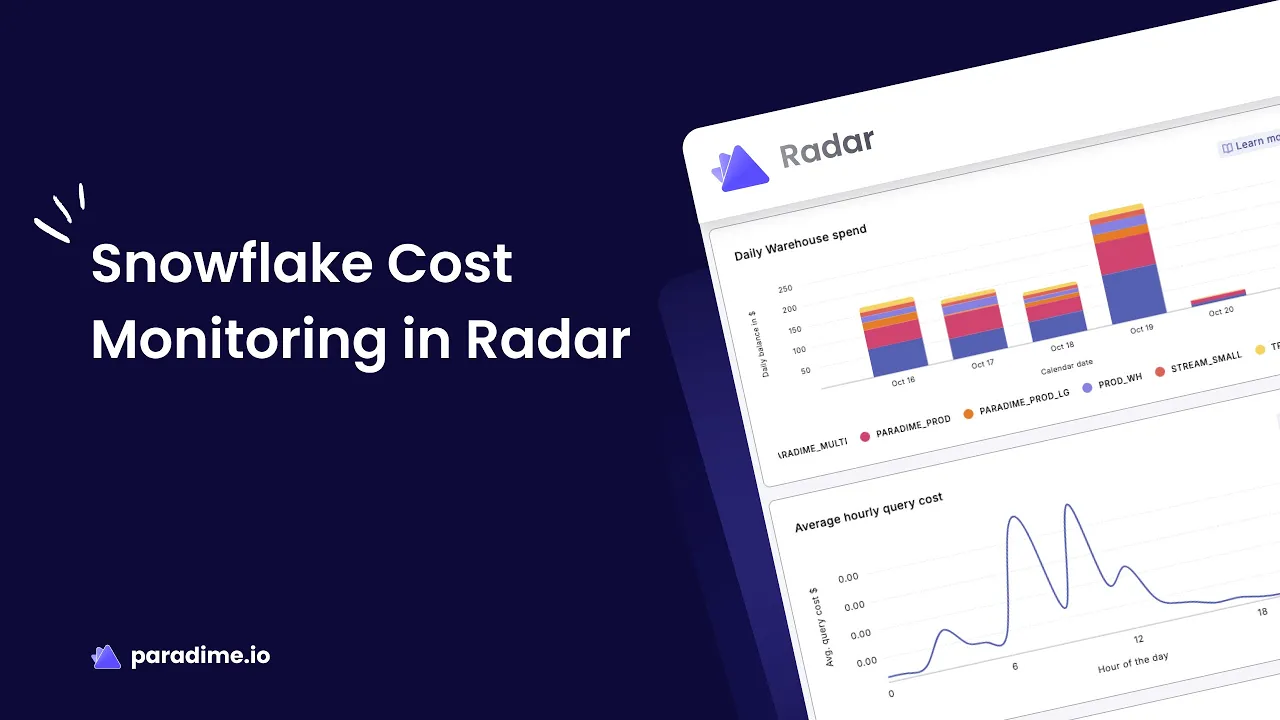
Daily Warehouse Spend Tracking
The Daily Warehouse Spend section reveals which warehouses contribute most to your overall costs. This view helps you quickly identify high-cost warehouses and unusual spending patterns that warrant investigation.
Track daily costs across all warehouses to establish baseline expectations. Notice which warehouses consistently run hot and which show sporadic usage. Sudden spikes often correlate with business activities—month-end reporting, product launches, or marketing campaigns—but unexpected increases signal potential issues.
Analyzing trends over time provides deeper insights. Compare week-over-week and month-over-month spending to understand seasonal patterns and growth trajectories. A warehouse that cost $500 last month but $1,200 this month deserves attention, especially if workload requirements haven't changed proportionally.
Use these insights to drive optimization decisions. Right-size warehouses based on actual usage patterns—if a large warehouse sits idle most of the day, downsize it. Configure auto-suspend settings to shut down warehouses after periods of inactivity, preventing costly idle time. Consider consolidating underutilized warehouses to improve efficiency and simplify management.
Query Spend Analysis by Segment
Understanding who drives costs is crucial for effective optimization. The Query Spend by Segment feature breaks down spending by user and role, revealing power users and cost-heavy query patterns.
This attribution enables targeted optimization. If one analyst accounts for 30% of warehouse spend, investigate their queries for optimization opportunities. Role-based analysis helps establish governance policies—perhaps data scientists need larger warehouses while analysts can use smaller ones.
Beyond user attribution, identify the most expensive individual queries. Sort by cost to find queries consuming hundreds or thousands of credits. These queries often contain inefficiencies—missing filters, unnecessary full table scans, or Cartesian joins that exponentially increase processing.
This visibility creates team-level cost accountability. Share insights across teams to build awareness of resource consumption. When analysts see their query costs, they naturally develop more cost-conscious habits—adding filters, limiting result sets, and testing queries on smaller datasets before running full analyses.
Identifying and Resolving Timeout Queries
Timeout queries represent a particularly insidious cost driver. Snowflake's default timeout settings allow queries to run for hours before failing, consuming credits the entire time without producing useful results.
The Snowflake Timeout Queries section in Radar identifies these expensive failures along with their associated costs. A query that times out after three hours might cost $50+ in wasted compute credits. Multiply that across multiple timeout queries per day, and you're looking at thousands of dollars in unnecessary spending monthly.
Use Radar's search function to find recurring timeout patterns. If the same query times out repeatedly, it indicates a fundamental inefficiency that needs addressing. Calculate the financial impact by summing timeout query costs over a week or month—this quantification helps prioritize optimization efforts and demonstrates ROI when fixed.
Prevent timeout issues through multiple strategies. Set appropriate timeout thresholds that fail queries faster when they're clearly not performing well—no query should run for hours without producing results. Refactor problematic queries by breaking complex operations into smaller steps, adding appropriate indexes, or restructuring joins. For legitimately complex workloads, assign them to larger warehouses that can process them efficiently rather than letting them struggle on undersized compute resources.
dbt Project Cost Management
For teams using dbt, understanding the cost implications of your data transformation pipelines is essential. The dbt Project Costs section provides visibility into individual query costs within dbt runs and overall production run expenses.
This granular view helps identify expensive dbt models that disproportionately drive costs. Some models might process massive datasets inefficiently or run full refreshes when incremental approaches would suffice. Focus optimization efforts on these high-cost models for maximum impact.
Implement incremental model strategies where appropriate. Instead of rebuilding entire tables on every run, incremental models only process new or changed records. This approach dramatically reduces compute time and costs, especially for large fact tables that receive daily or hourly updates. Configure incremental models to use merge, append, or delete+insert strategies based on your use case.
Warehouse assignment for dbt workloads offers another optimization lever. Use smaller warehouses for lightweight transformation tasks like creating views or processing small dimension tables. Reserve larger warehouses for heavy lifting—processing fact tables, complex aggregations, or models with extensive joins. Configure warehouse assignments at the model level in dbt to ensure each transformation uses appropriately sized compute resources.
Monitor production run costs to understand scheduled job expenses. Analyze whether jobs run more frequently than necessary—does that hourly refresh really need to be hourly, or would every two hours suffice? Balance freshness requirements against costs, finding the optimal frequency that meets business needs without overspending.
Best Practices for Ongoing Cost Monitoring
Effective cost optimization isn't a one-time project—it requires ongoing attention and discipline. Establish regular review cadences that fit your team's workflow. DevOps teams should monitor daily for anomalies, catching spikes or unusual patterns quickly. Weekly cost review meetings with analytics leadership ensure sustained focus on optimization. Monthly planning sessions identify long-term optimization opportunities and track progress against cost reduction goals.
Prioritize high-impact areas for maximum return on effort. Focus on the highest-cost users and roles first—optimizing queries from your top five cost drivers typically yields more savings than addressing dozens of minor contributors. Target the most expensive warehouses initially, as small improvements there generate significant savings. Distinguish between quick wins—adjusting warehouse sizes, enabling auto-suspend—and longer-term optimizations like query refactoring or architectural changes.
Set up proactive alerts and thresholds in Radar to catch issues before they become expensive problems. Configure budget threshold notifications that alert when daily or weekly spending exceeds expected levels. Enable anomaly detection to identify unusual spend patterns automatically—a warehouse that typically costs $100 daily suddenly costing $500 warrants immediate investigation.
Adopt data-driven decision making for warehouse configurations. Test optimization strategies with data rather than guessing—run experiments comparing performance and cost across different warehouse sizes. Measure the ROI of cost reduction initiatives by tracking savings against the time invested in optimization efforts.
Advanced Optimization Strategies
Once you've mastered basic monitoring, implement advanced strategies for deeper savings. Warehouse configuration optimization includes choosing the right base size for typical workloads, configuring multi-cluster warehouses to handle concurrency spikes efficiently, and fine-tuning auto-suspend settings—suspending too quickly can cause excessive warehouse restart costs, while suspending too slowly wastes credits on idle time.
Query pattern improvements offer substantial cost reductions. Leverage materialized views for frequently accessed aggregations rather than recomputing them every time. Utilize Snowflake's result caching to return previously computed results for identical queries instantly. Implement clustering keys on large tables to improve query performance and reduce scan costs.
Cross-functional collaboration amplifies optimization efforts. Educate analysts on cost-conscious querying practices—using LIMIT during development, avoiding SELECT *, and filtering early in queries. Establish query review processes where senior team members review expensive queries and suggest optimizations. Build a culture where cost optimization becomes part of everyone's responsibility, not just a finance or DevOps concern.
Measuring Success and ROI
Track key metrics to quantify your optimization efforts. Monitor month-over-month cost reduction percentages to ensure sustained progress. Calculate cost per query improvements to measure query optimization impact. Track warehouse utilization efficiency gains—are you getting more query throughput from the same or fewer resources?
Demonstrate value to stakeholders by building executive dashboards that show cost trends, savings achieved, and ongoing optimization initiatives. Quantify savings in concrete terms—"We reduced Snowflake spending by $15,000 monthly through warehouse right-sizing and query optimization." Connect cost reduction to business outcomes—savings reinvested in additional headcount, tools, or projects that drive revenue.
Conclusion
Paradime's Radar transforms Snowflake cost management from a reactive headache into a proactive optimization process. By providing visibility into daily warehouse spend, query-level cost attribution, dbt project expenses, and timeout query identification, Radar empowers analytics teams to make informed decisions that reduce spending while maintaining performance.
Start by completing the Radar setup and connecting your Snowflake account. Establish your monitoring routine—daily checks for anomalies, weekly reviews with your team, monthly optimization planning. Focus first on high-impact areas: expensive warehouses, high-cost users, and timeout queries. As you progress, implement advanced strategies like incremental dbt models, warehouse right-sizing, and query optimization.
The teams seeing 20%+ reductions in warehouse spending aren't cutting corners—they're using data to optimize intelligently. With Radar's comprehensive cost monitoring capabilities, you have everything needed to join them. Begin your optimization journey today and transform your Snowflake costs from a growing burden into a well-managed, continuously improving operation.