Git Lens and Git Blame: Advanced Code History and Search for Analytics Engineers
Aug 6, 2025
·
5
min read
Introduction
Paradime is an AI-powered workspace for analytics teams that consolidates the entire analytics workflow into one unified platform. Often described as "Cursor for Data," Paradime eliminates tool sprawl and accelerates data workflows by up to 10x. The platform features a Code IDE with DinoAI co-pilot, Paradime Bolt for production-grade orchestration, and Paradime Radar for comprehensive monitoring with column-level lineage. With native integrations to Looker, Tableau, Snowflake, and BigQuery, Paradime helps teams achieve 50-83% productivity gains, 20%+ warehouse cost reduction, and 25-50% faster development cycles—all while providing enterprise-grade Git visibility without requiring command-line expertise.
What are Git Lens and Git Blame?
Understanding Git Blame
Git blame is a fundamental version control feature that annotates each line of code with the last commit that modified it. For every line in a file, Git blame reveals who made the change, when it occurred, and which commit introduced it. This granular level of attribution transforms how teams understand their codebase's evolution.
In analytics engineering, where complex data transformations often span hundreds of SQL files and involve multiple team members, Git blame serves as an archaeological tool for understanding code history. Rather than assigning fault, it provides crucial context—helping you trace the origin of a transformation, understand the reasoning behind specific logic, or identify the right person to consult about a particular implementation.
Common use cases in analytics engineering include debugging production issues by identifying when specific logic was changed, onboarding new team members who need to understand codebase patterns, maintaining compliance audit trails, and coordinating work across distributed data teams.
Git Lens: Enhanced Git Visualization
Git Lens elevates basic Git functionality into a comprehensive visualization and navigation system. While traditional Git interfaces require command-line expertise and often involve context switching between different tools, Git Lens integrates powerful version control insights directly into your development environment.
For analytics engineers working in dbt projects, Git Lens provides a critical advantage: the ability to understand code history without leaving the IDE. Instead of memorizing Git commands or switching to a terminal, you access rich commit history, authorship details, and file evolution through an intuitive visual interface. This dramatically reduces the learning curve for SQL-focused analysts who may lack deep Git expertise but need reliable version control to manage complex data transformation pipelines.
Core Features of Git Lens in Paradime
Hover-Based Git Blame
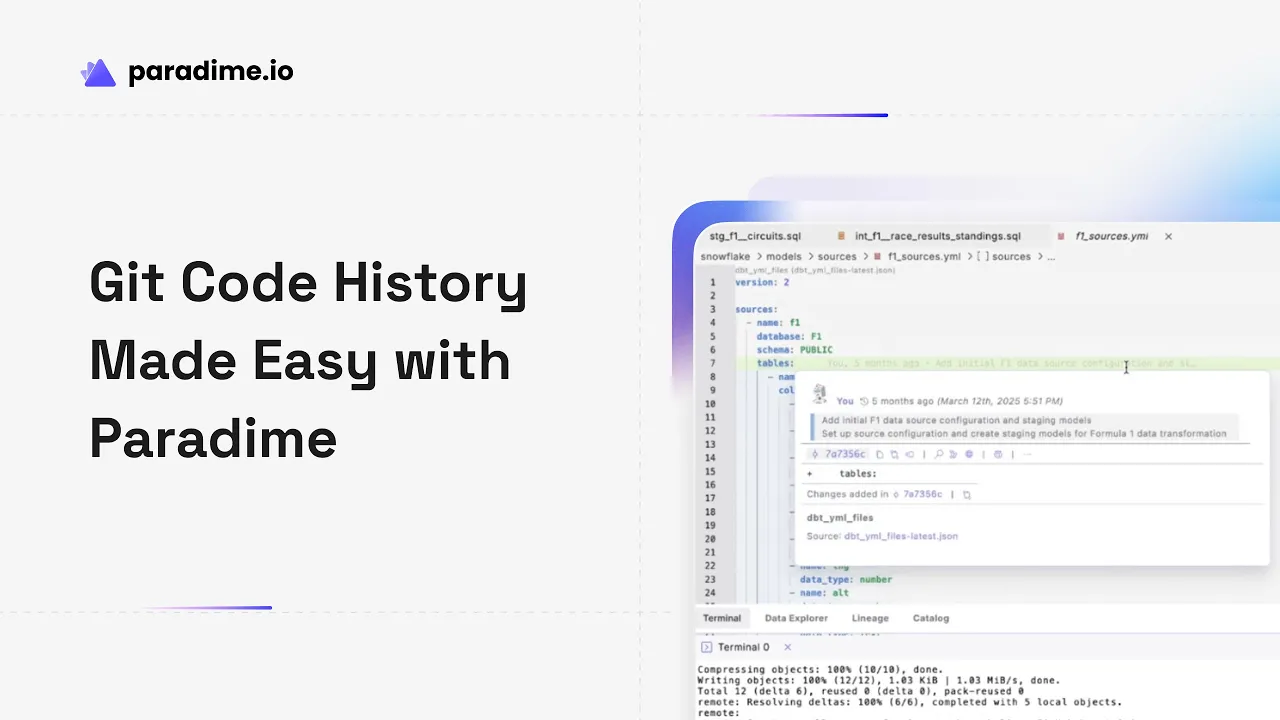
Paradime's Git Lens implementation displays inline blame annotations directly next to each line of code, showing the most recent author and commit date at a glance. When you hover over these annotations, additional commit details appear instantly—no need to run terminal commands or switch contexts.
This real-time visibility means you can understand code ownership and recent changes while actively developing. If you encounter an unfamiliar SQL transformation or need clarification on business logic, the hover feature immediately reveals who last touched that code and provides access to their commit message, giving you the context needed to make informed decisions.
Line-by-Line History Tracking
Beyond seeing the most recent change, Git Lens in Paradime allows you to explore the complete history of specific lines. By clicking the Git Lens icon and selecting a line of interest, you can view every commit that affected that particular piece of code over time.
This feature proves invaluable when debugging issues or understanding why certain transformations exist. You might discover that a seemingly odd SQL clause was added to handle a specific edge case three months ago, or that a join condition evolved through several iterations as business requirements changed. This historical perspective prevents you from accidentally reverting important fixes or removing logic that serves a non-obvious purpose.
File History Visualization
Git Lens provides a chronological view of all commits that affected a selected file, accessible through a dedicated tab in the left sidebar. This file-level perspective complements line-by-line tracking by showing how entire models evolved over time.
For dbt projects with dozens or hundreds of transformation models, file history helps you identify development patterns, understand major refactoring efforts, and see how models matured from initial implementation to production-ready assets. You can click any commit in the history to view detailed changes, making it easy to compare versions or understand the scope of past modifications.
Advanced Commit Search Capabilities
Rather than manually browsing through potentially thousands of commits, Paradime's Git Lens offers powerful search functionality. You can search commits by author name, message content, affected files, or even specific SHA identifiers.
This search capability integrates seamlessly with Paradime's AI-generated commit messages, which create naturally discoverable descriptions of changes. Instead of cryptic commit hashes, you can search for phrases like "updated customer segmentation logic" or "fixed revenue calculation" and immediately locate relevant changes—even if you weren't involved in the original work.
Benefits for Analytics Engineers
Collaboration Without Git Expertise
Traditional Git workflows require familiarity with commands like git blame, git log, and git diff—knowledge that many SQL-focused analysts lack. Paradime's Git Lens eliminates this barrier by providing a visual, intuitive interface that requires zero command-line expertise.
New team members can start understanding code history on day one without first completing a Git training course. Senior analysts who've spent years writing SQL but avoided version control can now engage with Git workflows naturally. This democratization of version control means your entire analytics team—regardless of technical background—can participate fully in collaborative development.
Improved Code Quality and Accountability
Git Lens creates natural accountability without fostering blame culture. When every line of code clearly shows its author and purpose, engineers write more thoughtfully and document their reasoning more carefully. Knowing that future team members will review your commit messages encourages clearer communication.
For data transformations that must meet compliance requirements or audit standards, Git Lens provides an automatic audit trail. You can demonstrate exactly who approved changes to sensitive calculations, when privacy-related logic was implemented, or how financial metrics evolved over time—all critical for SOC 2, GDPR, or industry-specific regulations.
Faster Debugging and Troubleshooting
When production data looks wrong, Git Lens helps you quickly identify when the issue was introduced. Rather than reviewing dozens of recent deployments, you can pinpoint the specific commit that changed relevant transformations.
Line-by-line history reveals whether a bug resulted from a recent change or represents a long-standing issue only now discovered. This context dramatically reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR) by focusing your investigation on the actual source of problems rather than chasing symptoms across multiple systems.
Enhanced dbt Project Management
Managing dbt projects involves coordinating model dependencies, maintaining consistent SQL patterns, and ensuring that changes to upstream models don't break downstream consumers. Git Lens helps by making dependencies and change patterns visible.
When modifying a staging model, you can review its history to understand how previous changes affected downstream marts. When establishing coding standards, you can examine how experienced team members structure their models and adopt proven patterns. This visibility fosters consistency and helps prevent the kind of technical debt that accumulates when teams lack clear visibility into their project's evolution.
Git Lens vs Traditional Git Interfaces
Limitations of Basic Git Tools
Command-line Git requires memorizing dozens of commands, understanding concepts like rebasing and cherry-picking, and interpreting text-based output that assumes developer familiarity. Standard Git UIs improve this slightly but still demand significant context switching—opening separate applications, navigating different interfaces, and translating results back to your code editor.
For analytics engineers focused on data transformation logic, this friction is costly. Every moment spent wrestling with Git syntax or switching between tools represents time not spent on actual analytics work. The learning curve is steep enough that many analysts simply avoid using advanced Git features, losing valuable insights about their codebase.
Paradime's Enterprise-Grade Git Visibility
Paradime integrates Git Lens directly into the dbt development environment, eliminating context switching entirely. The visual interface requires no prior Git knowledge—hover to see blame annotations, click to explore history, search to find commits.
Paradime's AI-powered commit message generation ensures that even routine commits become meaningful, searchable documentation. Rather than generic messages like "updated model," you get descriptive summaries that make your project's history genuinely useful for future reference.
Best Practices for Using Git Lens and Git Blame
Implementing Effective Version Control Workflows
Start by establishing commit message conventions that provide genuine value. Rather than "fixed bug" or "updated query," write messages that explain what changed and why: "Added COALESCE to handle null revenue values from legacy systems." Paradime's AI assistance makes this easier by generating context-aware suggestions.
Adopt descriptive branch naming that reflects the work being done: feature/customer-churn-model or fix/revenue-calculation-timezone. When combined with Git Lens's search capabilities, this creates a project history that reads like documentation rather than cryptic technical logs.
Optimizing Team Collaboration
Use Git blame data to identify code owners for questions and reviews, but frame it constructively. Rather than "who broke this," ask "who can help me understand this logic." Create a culture where commit history is viewed as shared knowledge rather than evidence for fault-finding.
Document your reasoning in commit messages, knowing that future team members will rely on this context when they encounter your code months or years later. This investment pays dividends when those team members can solve problems independently rather than interrupting current work with historical questions.
Integrating with dbt Development
Version control your dbt models at logical change points—after completing a new transformation, fixing a bug, or refactoring for performance. Atomic commits that represent coherent units of work create more useful history than massive commits that bundle unrelated changes.
When schema changes occur, use Git Lens to understand how previous schema migrations were handled. This helps maintain consistency in how your team approaches evolution of data models over time, reducing the risk of breaking changes that surprise downstream consumers.
Real-World Use Cases
Debugging Production Issues
When quarterly revenue numbers don't match expectations, Git Lens helps you trace the calculation logic back through every modification. You discover that three weeks ago, a commit changed how exchange rates are applied—a well-intentioned fix for European currencies that inadvertently affected USD calculations. The commit message and author information give you everything needed to understand and reverse the problematic change.
Onboarding New Team Members
New analytics engineers can explore your dbt project's Git history to understand patterns and conventions without relying entirely on senior team members. They see how experienced engineers structure staging models, handle slowly changing dimensions, or implement complex window functions. This self-service learning accelerates onboarding while reducing interruptions to existing team members.
Compliance and Auditing
When auditors ask how financial calculations are controlled, Git Lens provides complete documentation of who changed each metric, when changes were approved, and what reasoning justified the modifications. This audit trail—generated automatically through normal development workflows—satisfies regulatory requirements without additional documentation overhead.
Code Review and Quality Assurance
During pull request reviews, Git Lens helps reviewers understand how proposed changes relate to historical patterns. If someone refactors a complex calculation, reviewers can see the original implementation's history to ensure the new version preserves important edge case handling or business logic that might not be immediately obvious.
Getting Started with Git Lens in Paradime
Setting Up Your Environment
Access Git Lens features through the dedicated icon in Paradime's Code IDE left sidebar—no configuration required. The interface works identically whether you're using Git Lite or Git Advanced modes, ensuring consistent functionality regardless of your chosen Git workflow style.
Connect your dbt project to a Git repository through Paradime's workspace settings, and Git Lens automatically begins tracking your code history. Existing repositories bring their complete commit history, giving you immediate access to years of development context.
Essential Commands and Features
Start by hovering over code to see inline blame annotations—the most frequent Git Lens interaction. When you need deeper context, click the Git Lens icon and explore the File History tab to see all commits affecting your current file. Use Line History to understand how specific transformations evolved.
Access the Search & Compare feature to find commits across your entire project. Search by author to see a colleague's recent work, by message to locate specific changes, or by file to understand how particular models have evolved.
Tips for Maximizing Productivity
Make Git Lens part of your debugging workflow—before diving into complex troubleshooting, check when potentially problematic code last changed. Use file history to understand context before refactoring legacy models. Leverage commit search to find examples of how your team has handled similar problems in the past.
Combine Git Lens with Paradime's other features: use DinoAI co-pilot for intelligent commit message generation, leverage column-level lineage to understand downstream impacts of changes, and integrate Git Lens insights into your code review process for more informed feedback.
Conclusion
Git Lens and Git Blame in Paradime bring enterprise-grade version control visibility to analytics engineers without requiring deep Git expertise. By providing intuitive, visual tools for tracking code history, understanding changes, and collaborating effectively, these features enable data teams to work faster, debug more efficiently, and maintain higher code quality. Whether you're debugging production issues, onboarding new team members, or ensuring compliance, Paradime's Git Lens functionality transforms how analytics teams interact with version control—making Git accessible, powerful, and integrated seamlessly into your dbt development workflow.