Discover PII Gaps Using Column-Level Lineage
Nov 17, 2025
·
5
min read
Introduction
In today's data-driven landscape, organizations face a critical challenge: managing personally identifiable information (PII) across increasingly complex data pipelines while maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. A single untagged PII field flowing through your data warehouse can expose your organization to hefty fines, reputational damage, and security vulnerabilities.
Paradime is an AI-powered workspace for analytics engineers that consolidates the entire analytics workflow. Often described as "Cursor for Data," Paradime eliminates tool sprawl and fragile local setups while providing clarity about code change impacts. With features like DinoAI (an AI co-pilot for SQL), Paradime Bolt for production-grade orchestration, and advanced column-level lineage capabilities, Paradime helps data teams achieve 50-83% productivity gains and faster development cycles while ensuring data governance and compliance.
Column-level lineage has emerged as a game-changing solution for discovering PII gaps—those untagged or misclassified sensitive data fields that slip through governance processes. This comprehensive guide explores how to leverage column-level lineage to identify, track, and manage PII throughout your data ecosystem, ensuring your organization stays compliant and your customers' data remains protected.
What is PII and Why Does It Matter?
Understanding Personally Identifiable Information
PII encompasses any data that can identify an individual, either directly or indirectly. Direct identifiers include obvious elements like names, social security numbers, email addresses, and phone numbers. Indirect identifiers—such as IP addresses, device IDs, location data, and dates of birth—can identify individuals when combined with other data points.
Sensitive PII requires extra protection and includes financial records, health information, and biometric data. It's worth noting that terminology varies by region: what's called PII in the United States may be referred to as "personal data" under GDPR in the European Union.
The Regulatory Landscape
Data privacy regulations have proliferated globally, with GDPR setting strict requirements for EU residents' data and CCPA establishing consumer privacy rights in California. Industry-specific regulations like HIPAA (healthcare), PCI-DSS (payment card data), and SOX (financial reporting) impose additional compliance obligations.
Non-compliance carries severe consequences: GDPR violations can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Beyond financial penalties, organizations face reputational damage, customer trust erosion, and operational disruptions from data breaches—all of which can create lasting competitive disadvantages in increasingly privacy-conscious markets.
The Power of Column-Level Lineage
What Makes Column-Level Lineage Essential
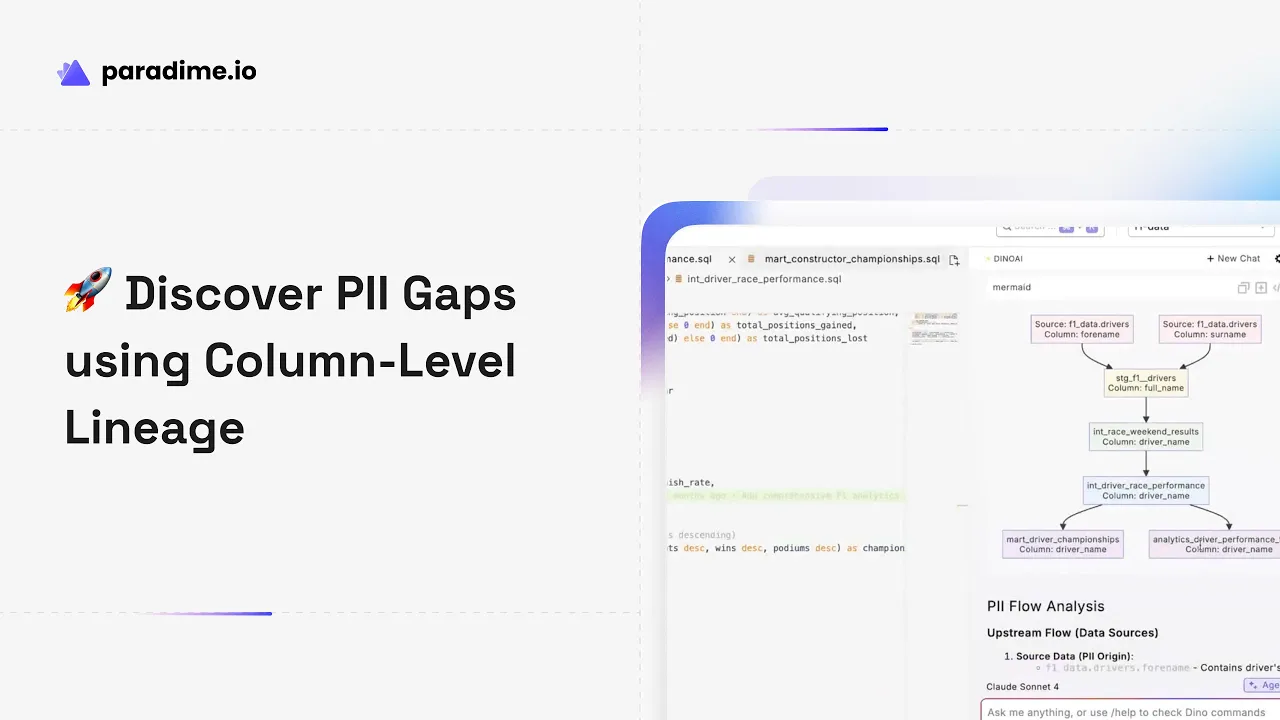
Column-level lineage tracks how individual data fields evolve through data pipelines, providing granular visibility that table-level lineage cannot match. By parsing every SQL statement in your data warehouse, it constructs an intuitive graph showing exactly how data is created, transformed, and consumed at the column level.
This capability becomes invaluable when dealing with PII. You can select a specific column containing sensitive information and visualize only the columns on its downstream path, revealing where that information flows throughout your data ecosystem—from source systems through transformations to final dashboards and reports.
Key Benefits for Data Teams
Column-level lineage delivers multiple advantages: impact analysis helps you understand downstream effects before making changes; root cause analysis accelerates debugging by tracing issues to their source; data quality monitoring tracks transformations for accuracy; and compliance auditing provides proof of data handling practices to regulators. Perhaps most importantly, it automates documentation maintenance, ensuring your data dictionaries remain current without manual effort.
Modern data platforms integrate column-level lineage with dbt projects and BI tools like Looker, Tableau, and Power BI, enabling real-time monitoring with automated alerts through state-aware orchestration systems.
The Challenge of PII Gaps
What Are PII Gaps?
PII gaps represent the silent compliance risk lurking in your data pipelines: untagged or unclassified PII columns in your data warehouse, sensitive information flowing without proper governance, and inconsistent PII handling across data sources. Most concerning is "shadow PII"—fields that contain personal data but aren't recognized as such by your governance systems.
Common Causes and Risks
Several factors contribute to PII gaps. Rapid pipeline development often outpaces governance checks, while many organizations lack automated PII detection tools. Multiple data sources with inconsistent tagging practices, schema changes introducing new PII fields, third-party data integrations, and legacy systems without modern data catalogs all compound the problem.
The risks are substantial: compliance violations and regulatory penalties, unauthorized access to sensitive data, security vulnerabilities, inability to honor data subject rights (like GDPR's right to deletion), failed audits, and incomplete data retention policies. Each gap represents a potential breach waiting to happen.
Discovering PII Gaps with Column-Level Lineage
Automated Detection Techniques
Modern PII discovery combines multiple approaches. Pattern matching uses regular expressions to identify emails, phone numbers, and social security numbers. Statistical analysis helps detect indirect identifiers. Metadata-based detection examines column names and descriptions for PII indicators. Machine learning-based classification can identify sensitive data even in fields with non-obvious names.
Effective PII detection systems scan structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data formats, including free-text fields where PII often hides. They balance precision (minimizing false alarms) with recall (capturing most PII) to create comprehensive yet manageable inventories.
Tracing PII Through Transformations
Column-level lineage excels at following individual columns from source to BI layer. It identifies derived PII fields created through concatenations or calculations—like a "full_name" field combining first and last names—and tracks PII propagation through joins and unions. This visibility helps detect when PII is inadvertently exposed in non-secure locations.
You can also understand how transformations protect PII through masking, hashing, or tokenization. More importantly, lineage reveals when these protections aren't applied, flagging potential compliance issues before they reach production dashboards.
Building a Comprehensive PII Inventory
With column-level lineage, you can create automated catalogs of all PII fields, mapping each to relevant compliance requirements. Document data retention and deletion policies at the field level, maintain lineage documentation for audit trails, and set up continuous monitoring for new PII fields as your pipelines evolve.
This living inventory becomes your single source of truth for PII governance, enabling quick responses to data subject access requests, demonstrating compliance during audits, and supporting data minimization efforts.
Implementing PII Discovery: A Practical Approach
Step 1: Inventory and Enable Lineage
Begin by identifying all data sources in your pipeline and cataloging tables and columns across sources. Document known PII fields and assess data source sensitivity levels. Then enable column-level lineage tracking in your data platform, configuring integrations with BI tools and validating lineage accuracy.
Step 2: Run Automated Scans and Trace PII
Deploy PII detection algorithms across your inventory, reviewing and validating detected PII while addressing false positives and negatives. Follow PII columns through transformations, identifying unexpected locations where sensitive data appears. Document PII flow paths and assess exposure at each stage.
Step 3: Identify Gaps and Implement Monitoring
Compare your actual PII inventory to what you expected to find. Flag untagged or misclassified PII, prioritizing gaps by risk level and creating remediation action plans. Establish continuous monitoring with automated alerts for new PII, schedule regular audits, and track PII governance metrics to drive improvement.
How Paradime Transforms PII Governance
AI-Powered PII Discovery
Paradime's column-level lineage capabilities integrate seamlessly with DinoAI to revolutionize PII governance. DinoAI analyzes how PII fields flow through entire pipelines, tracing columns back to sources and identifying composite fields created by concatenating first and last names or other PII elements.
When DinoAI checks downstream usage of PII fields, it flags when they reach analytics models unmasked—a potential compliance issue. As one Paradime demonstration shows: "This is actually saying okay, you have a potential issue. We have this column across all our data pipeline and it's not masked anywhere."
From Detection to Active Governance
Paradime goes beyond identification to provide active governance assistance. When asked to anonymize a field, DinoAI proposes specific implementations using hash-based anonymization or other techniques, generates actual code changes, and explains where those changes should be applied. It can even draft pull request descriptions documenting compliance changes for audit trails.
This transforms column-level lineage from passive documentation into active governance, helping teams implement proper masking and suggesting where anonymization should occur. Teams can generate fresh compliance reports on demand, automatically identify PII fields lacking proper masking, and receive AI-generated remediation recommendations.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Paradime enables real-time alerts for PII exposure risks through integrations with PagerDuty, DataDog, and Slack. Automated compliance checks in CI/CD pipelines catch issues before they reach production, while dashboard monitoring tracks PII access patterns. This proactive approach prevents compliance violations rather than discovering them after the fact.
Advanced PII Management Strategies
Data Masking and Anonymization
Effective PII protection requires understanding various techniques. Static data masking permanently alters data in non-production environments, while dynamic masking applies protection in real-time based on user permissions. Tokenization replaces PII with tokens that can be remapped to original values, providing reversible anonymization. Hashing offers one-way protection when you need to verify data without exposing it. For testing and development, synthetic data generation creates realistic datasets without real PII.
Access Control and Security
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict PII access by job function. Attribute-based access control (ABAC) provides even more granular permissions based on multiple factors. Column-level security in data warehouses like Snowflake and BigQuery ensures users only see authorized fields. Combine these with encryption at rest and in transit, plus secure data sharing practices, to create defense-in-depth protection.
Data Retention and Lifecycle Management
Define retention periods by data type based on regulatory requirements and business needs. Automated deletion workflows help honor GDPR's "right to erasure" and similar requirements. Consider backup and archival implications—deleted data must disappear from all copies. Implement comprehensive data lifecycle management to ensure PII is retained only as long as necessary.
Measuring Success and Building a Governance Culture
Key Metrics for PII Governance
Track the percentage of cataloged PII fields to measure inventory completeness. Monitor time to detect new PII in pipelines—shorter times indicate more effective governance. Count PII access violations and incidents to identify weak points. Track compliance audit scores and mean time to remediate PII gaps as indicators of program maturity.
Creating Compliance Documentation
Maintain comprehensive audit trails for regulatory review. Create compliance reports for stakeholders demonstrating adherence to GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations. Document data handling procedures clearly, showing continuous improvement in governance practices. This documentation proves invaluable during audits and investigations.
Fostering Data Governance Culture
Technology alone doesn't ensure compliance—people and processes matter too. Train data teams on PII handling best practices. Establish governance champions who advocate for privacy. Incorporate PII checks into standard development workflows so they become second nature. Create feedback mechanisms for policy updates, ensuring your governance framework evolves with your organization.
Conclusion: Taking Action on PII Gaps
PII gaps represent one of the most significant compliance risks facing modern data organizations. Column-level lineage provides the visibility needed to discover these gaps, trace sensitive data through complex pipelines, and implement effective governance controls.
Modern platforms like Paradime transform this capability from passive documentation into active governance assistance, using AI to identify issues, recommend solutions, and even generate remediation code. By automating PII detection and continuous monitoring, organizations can prevent compliance violations rather than discovering them during audits.
Start by assessing your current PII governance maturity. Implement column-level lineage in your data platform, beginning with high-risk data sources and pipelines. Build iteratively toward comprehensive PII management, recognizing that governance is an ongoing journey rather than a one-time project.
The stakes are high: regulatory fines, customer trust, and competitive positioning all depend on effective PII management. But with the right tools and practices, you can turn PII governance from a compliance burden into a competitive advantage, demonstrating your commitment to customer privacy while enabling safe, responsible data use throughout your organization.