Creating dbt Jobs in Paradime Bolt: Complete Configuration Guide
Jul 16, 2025
·
5
min read
Introduction
Paradime is an AI-powered workspace for analytics teams that consolidates the entire analytics workflow into one platform. With Paradime Bolt, teams can build production-grade, state-aware orchestration for dbt™ with declarative scheduling, CI/CD, and automated test runs. This eliminates tool sprawl and delivers 10x faster shipping speed with 50-83% productivity gains compared to fragmented toolchains.
What is Paradime Bolt and Why Use It for dbt™ Scheduling
Paradime Bolt is a production-grade orchestration system built specifically for dbt™, offering state-aware scheduling with declarative YAML configuration. It eliminates the complexity of setting up and maintaining separate orchestration tools like Airflow, bringing scheduling directly into your analytics workspace.
The key benefits are compelling: maintain fresh production data on consistent schedules, execute CI/CD and production pipelines efficiently, and identify deployment issues quickly with native integrations and custom webhooks. Before creating your first Bolt schedule, ensure your scheduler environment is connected to your data warehouse provider, your Git repository is integrated with Paradime, and you have the appropriate workspace permissions.
Understanding Schedule Types in Paradime Bolt
Bolt offers three distinct schedule types, each designed for specific use cases:
Standard Schedules are traditional scheduled runs ideal for regular production pipelines. Use these for your core data transformation workflows that need to run on a consistent cadence.
Deferred Schedules leverage manifest comparison between runs to optimize execution time and compute costs. By referencing previous job states, they only run changed models and their dependencies—a powerful feature for large dbt projects where full rebuilds are unnecessary.
Turbo CI Schedules provide rapid continuous integration testing for pull requests. When enabled, Turbo CI automatically builds modified models and their dependencies in a temporary schema, validating code changes before they reach production.
Creating Your First dbt™ Job in Paradime Bolt
Navigate to Bolt from your Paradime workspace to access the scheduling interface. The Bolt UI provides a streamlined setup process organized into clear configuration steps.
Start with basic schedule configuration by giving your schedule a clear, descriptive name like "daily-backup-prod" or "weekly-data-cleanup." While optional, adding a description helps document the schedule's purpose for your team. Assign an owner email for accountability and select the appropriate Git branch—typically main or master for production schedules, or feature branches for development workflows.
When choosing your schedule type, consider your needs: Standard schedules work for most use cases, Deferred schedules reduce costs for large projects with incremental changes, and Turbo CI schedules automate pre-merge validation.
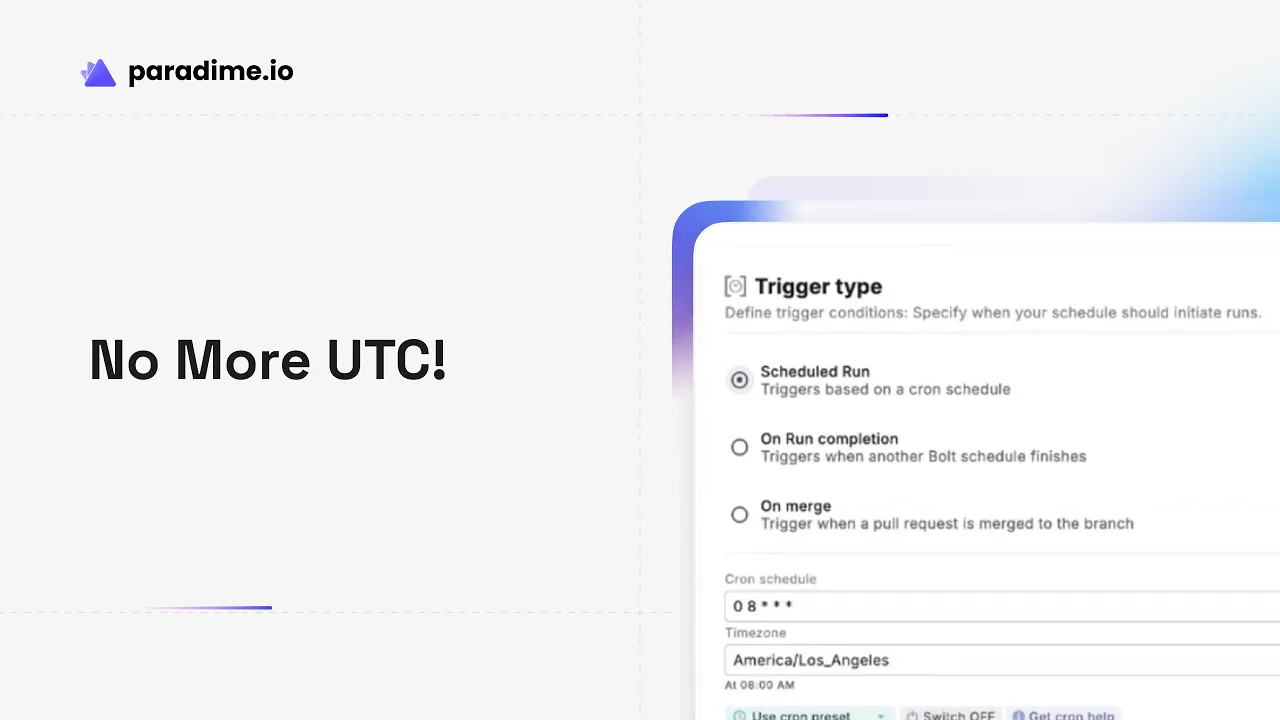
Configuring Time Zones for Bolt Schedules
Timezone configuration matters more than you might think, especially for globally distributed teams. Bolt defaults to UTC, which works well for consistency but may not align with your business hours.
For Scheduled Run triggers, you can select a custom timezone to ensure schedules execute during the right hours for your location. This is particularly important for schedules that need to complete before business starts or that depend on data arriving from specific regions.
When coordinating schedules across teams in different locations, document your timezone choices in the schedule description. This simple practice prevents confusion when troubleshooting why a schedule ran at an unexpected time or when coordinating dependent workflows across regions.
Setting Up Trigger Types for Your dbt™ Jobs
Bolt offers four trigger types that determine when your schedules execute:
Scheduled Run Triggers use cron expressions to define when jobs run. Bolt provides preset cron options for common patterns, but you can also write custom expressions. For complex schedules, leverage tools like crontab.guru to validate your cron syntax. Set the cron schedule to OFF if you want manual/ad-hoc runs only.
On Run Completion Triggers create job dependencies by executing when a specified schedule finishes. Select the workspace name, choose the Bolt schedule to monitor, and pick the trigger event: Passed (runs only after success), Failed (runs only after failures), or Both. This enables building sequential pipeline workflows where downstream jobs wait for upstream dependencies.
On Merge Triggers automate deployments after code merges into designated branches. This requires GitHub integration—your Paradime workspace must be connected to your GitHub repository with the GitHub App installed. Once configured, schedules execute automatically when pull requests merge, perfect for production deployment workflows.
Bolt API Triggers enable programmatic schedule execution via REST API endpoints. To configure API-only triggering, select Scheduled Run as the trigger type and click OFF. This is ideal for integrating Bolt with external systems or building custom orchestration logic.
Configuring Command Settings for dbt™ Execution
Command settings define what actually runs when your schedule triggers. Bolt executes commands sequentially, and by default, subsequent tasks are skipped when a command completes with an error.
However, three important exceptions exist: Source Freshness commands followed by tasks using the source_status:fresher selector method will execute regardless of freshness check failures. Elementary CLI commands always execute to send alerts and generate reports on test failures. Monte Carlo commands run even after errors to upload dbt™ resources.
Bolt supports an extensive range of command types beyond standard dbt™ commands (run, test, seed, snapshot, etc.). You can execute Python scripts for custom transformations, Elementary commands for data observability, and trigger BI tool refreshes for Lightdash, Tableau, and Power BI. Data pipeline triggers for Airbyte and Fivetran enable end-to-end workflow orchestration, and you can even toggle other Bolt schedules with the Paradime Bolt Schedule Toggle command.
When creating custom command combinations, order matters. A typical pattern might be: dbt seed → dbt run → dbt test → dbt snapshot → Elementary report generation. This ensures data loads before transformations, tests validate results, and observability tools receive the latest information.
Setting Up Notifications for dbt™ Job Monitoring
Effective notification configuration is crucial for production data pipelines. Bolt offers three notification types: Success notifications confirm jobs are running as expected, Failure alerts enable immediate incident response, and SLA notifications warn when jobs exceed specified runtime thresholds.
To configure notifications, navigate to the Bolt UI, select your schedule, and click Edit. In Notification Settings, click Add destination and choose from three channels: Email, Slack, or Microsoft Teams. Slack and Teams require initial setup through Paradime's integration guides.
For SLA monitoring, set an appropriate threshold in minutes—for example, 30 minutes for a job that typically completes in 15 minutes. When a schedule exceeds this threshold, Bolt triggers an SLA notification, helping you catch performance degradation before it impacts downstream systems.
Bolt also provides workspace-level system alerts for critical infrastructure issues: Bolt Parse Errors when schedule configurations are invalid, OOM (Out of Memory) Runs when jobs exceed available memory, Git Clone Failures when repository access fails, and 24-hour Run Timeouts when jobs exceed Bolt's maximum execution window.
Environment Variables and Override Configuration
Environment variables enable schedule-specific configurations without modifying your dbt code. While Bolt provides standard environment variables for all schedules, you can override these values for specific schedules when different jobs need different settings.
Use environment variable overrides sparingly and document them clearly in your schedule descriptions. This prevents confusion when debugging issues that behave differently across schedules. Always test variable overrides thoroughly before deploying to production to ensure they interact correctly with your dbt models.
Managing and Monitoring Your Bolt Schedules
After deployment, ongoing management ensures your schedules remain healthy. The Bolt UI provides comprehensive execution history showing run logs, results, and execution metrics. Use this data to identify patterns in failures and optimize schedule performance.
Editing existing schedules is straightforward—navigate to your schedule, click Edit, make your changes, and click Deploy. Test significant changes in a non-production schedule first when possible. If a schedule update causes issues, you can quickly roll back by reverting to previous configuration settings.
Toggle schedules on or off to temporarily disable them without deleting the configuration. This is useful when pausing pipelines during maintenance windows or troubleshooting dependencies. You can even automate schedule toggling using Paradime Bolt Schedule Toggle commands within other schedules.
Performance optimization is an ongoing process. Analyze schedule runtime trends to identify models that have become slower over time. Optimize dbt™ models with incremental strategies, appropriate materializations, and efficient SQL. Balance schedule frequency with resource usage—not every job needs to run hourly if daily is sufficient for business needs.
Advanced Bolt Features and Integrations
Schedules as Code brings the power of version control to your orchestration configuration. The paradime_schedules.yml file in your dbt project root enables defining schedules declaratively alongside your dbt code. This approach provides version history, code review for schedule changes, and the ability to manage schedules across environments programmatically.
Bolt's native integration capabilities extend beyond dbt™ commands. Trigger integrations connect Bolt to tools like Airbyte and Fivetran, enabling end-to-end data pipeline orchestration. Custom webhook implementations allow connecting virtually any system to your Bolt workflows.
Pre-configured templates accelerate schedule creation for common patterns. Use templates as starting points, customize them for your specific needs, and build a library of reusable schedule patterns that your team can deploy consistently.
Best Practices for Production dbt™ Scheduling
Separate development and production schedules clearly—never run production jobs against development branches or vice versa. Implement appropriate job dependencies using On Run Completion triggers to ensure data flows through your pipeline in the correct order. Balance data freshness requirements with resource costs; running schedules more frequently increases warehouse costs without always delivering proportional business value.
Design your notification strategy to avoid alert fatigue. Send failure notifications to the entire team, but reserve SLA alerts for schedule owners who can investigate performance issues. Document incident response procedures so team members know who to contact and what steps to take when schedules fail.
Test schedules thoroughly before production deployment. Use Turbo CI to validate code changes pre-merge, and run new schedules manually several times before enabling automated triggers. Monitor schedule health over time using Bolt's execution history and logging features.
Document schedule purposes and owners in descriptions, maintain a schedule inventory that maps business requirements to specific schedules, and implement change management processes that require code review for schedule modifications.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When schedules fail, start by investigating the run logs in Bolt's execution history. Common error patterns include credential issues (check warehouse connection), dbt compilation errors (validate model SQL), and dependency failures (verify upstream schedules completed successfully).
Notification delivery problems typically stem from integration configuration. Verify Slack and Teams webhooks are properly connected, test notification channels with a manual trigger, and check that email addresses are correct and can receive external messages.
Timezone confusion causes schedules to run at unexpected times. Remember that Bolt defaults to UTC, so a schedule set for "9 AM" runs at 9 AM UTC, not your local time. Verify the timezone setting on your Scheduled Run triggers and clearly document expected run times in local time zones in schedule descriptions.
Performance and timeout issues require optimization at multiple levels. Address long-running jobs by optimizing dbt™ model SQL, using incremental materializations for large tables, and breaking monolithic schedules into smaller dependent jobs. Prevent OOM errors by reducing memory-intensive operations or requesting increased resources. If jobs approach the 24-hour timeout limit, they likely need architectural changes—consider breaking the workflow into multiple dependent schedules or optimizing the underlying transformations.
Conclusion
Paradime Bolt transforms dbt™ scheduling from a complex orchestration challenge into a streamlined, integrated workflow. By understanding schedule types and when to use them, properly configuring triggers, commands, and notifications, and implementing robust monitoring and maintenance practices, data teams can build reliable production pipelines that deliver fresh, trusted data to their organizations.
Start by implementing your first production schedule using the Standard type with a simple Scheduled Run trigger. As you gain confidence, expand to more complex workflows with dependencies, deferred execution, and integrated observability. Explore advanced Bolt features like Schedules as Code and native integrations to unlock even greater efficiency and control.
For additional support, explore Paradime's comprehensive documentation, engage with community support channels, and take advantage of training and onboarding materials to accelerate your team's Bolt adoption journey.