Building Your First dbt Model in Paradime
Oct 8, 2025
·
5
min read
Introduction
Paradime is an AI-powered analytics workspace, often described as 'Cursor for Data', that consolidates the entire analytics workflow into one seamless platform. With features like DinoAI co-pilot that writes SQL and generates documentation, Paradime Bolt for production-grade dbt orchestration, and Paradime Radar for real-time monitoring with column-level lineage, teams are achieving 50-83% productivity gains and 25-50% faster development cycles. Paradime integrates natively with Looker, Tableau, and the modern data stack, making it the ideal environment for analytics engineering.
Getting Started with Your First dbt Model
Understanding the Paradime dbt Environment
Before diving into model creation, it's essential to understand Paradime's dbt-native platform. Unlike traditional development environments, Paradime provides a fully integrated workspace that combines data exploration, dbt development, and production deployment capabilities. With over 40 integrations including MotherDuck, Snowflake, Looker, Airflow, and Github, you can build comprehensive data pipelines without switching contexts.
The platform's intuitive Code IDE eliminates the friction typically associated with analytics engineering setup. Everything you need—from SQL editing to Git version control to data preview—lives in a single, cohesive interface designed specifically for dbt workflows.
Initializing Your dbt Project
The first step in building your dbt model is initializing a new project within Paradime. This process creates the foundational structure needed for your analytics engineering work and typically takes about 10 minutes from start to finish.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
Paradime developer or admin permissions
A Git repository connected to Paradime (either an existing dbt repository or a new one)
Access to your data warehouse
Creating the Project Framework
To initialize your dbt project, open the Terminal in Paradime's Code IDE and run:
This command launches an interactive setup process that:
Creates a new branch called
initialize-dbt-projectPrompts you to name your dbt project (e.g.,
demo_project)Generates the complete dbt project skeleton with all necessary folders and files, including the core
dbt_project.ymlconfiguration fileOffers to automatically generate
sources.ymlfiles
Naming Your Project
When prompted, choose a project name that is descriptive and follows your team's naming conventions. A clear, consistent naming strategy ensures better organization and collaboration as your analytics engineering practice scales. Consider names like sales_analytics, customer_insights, or finance_reporting that immediately communicate the project's purpose.
Building Your Modeling Architecture
Creating .yml Configuration Files
Configuration files are the backbone of your dbt project architecture. These YAML files define model properties, tests, and documentation that ensure data quality and maintainability.
Generating Sources
During project initialization, Paradime offers to automatically generate sources.yml files that define how dbt interacts with your raw data sources. This process is remarkably streamlined:
Paradime automatically fetches available databases and schemas from your connected data warehouse
Use arrow keys to select a database and press Enter
Navigate through schemas using arrow keys, press
>to select, then Enter to confirmParadime generates files using the naming convention
sources_.yml
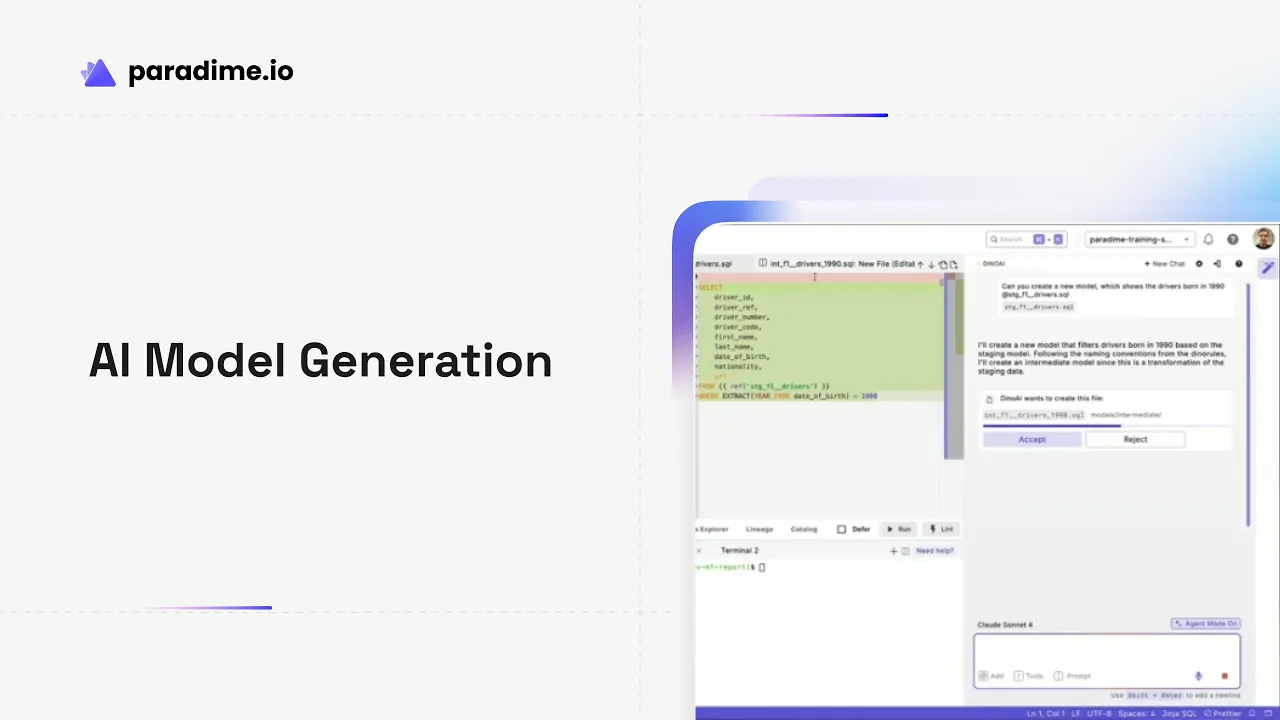
You can rename these files to match your preferred conventions, or generate sources later using DinoAI's intelligent capabilities.
Model Properties and Metadata
Beyond sources, you'll create additional YAML files to document your models. These files should include:
Model descriptions: Clear explanations of what each model does and why it exists
Column definitions: Documentation of each column's meaning, data type, and business logic
Metadata tags: Labels that help organize and categorize models across your project
Well-structured YAML files make your data transformations transparent and understandable to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Defining Tests and Constraints
Implementing data quality tests in your configuration files helps catch issues early and ensures your models produce reliable results. Common test configurations include:
Uniqueness tests: Ensure primary keys contain no duplicates
Not-null tests: Verify that critical columns never contain null values
Referential integrity tests: Validate that foreign keys reference existing records
Custom business logic tests: Confirm domain-specific rules are enforced
These tests run automatically as part of your transformation pipeline, providing continuous validation of your data quality.
Structuring Your Data Model
Building an effective data model requires careful planning of your transformation logic, dependencies, and outputs.
Model Layering Strategy
The dbt community has established a proven layering approach that organizes models into three distinct tiers:
Staging Layer: This is where raw data enters your dbt project. Staging models have a 1-to-1 relationship with source tables and perform light transformations like:
Renaming columns to consistent standards
Casting data types
Performing basic data cleaning
Using the
{{ source() }}macro to reference raw tables
Staging models are the only place you'll use the source macro, creating atomic building blocks for downstream transformations.
Intermediate Layer: These purpose-built models sit between staging and final outputs, centralizing reusable transformation logic. Intermediate models:
Combine multiple staging models
Apply complex business logic
Create reusable components that prevent code duplication
Typically materialize as views to minimize storage overhead
Marts Layer: Also called the semantic or consumption layer, marts contain finalized models ready for business intelligence tools and end users. These models:
Represent specific business concepts (customers, orders, revenue)
Are often materialized as tables for query performance
Include comprehensive documentation and testing
Serve as the "single source of truth" for analytics
This layered approach creates maintainable pipelines where changes cascade predictably through your transformation logic.
Writing Transformation Logic
When writing SQL transformations within your dbt models, leverage dbt's jinja templating syntax to create dynamic, reusable code:
The {{ ref() }} macro creates dependencies between models, allowing dbt to automatically determine the correct execution order. This dependency graph is central to dbt's power and ensures your models build in the right sequence.
Working with Data: Preview and Validation
Previewing Data Before dbt Run
One of Paradime's most powerful features is the ability to preview your data transformations before executing a full dbt run. This capability saves significant time and computational resources by letting you validate logic on sample data.
Using the Data Explorer
To preview your model's output:
Open any SQL file in the Code IDE editor
Click the Data Explorer icon in the command panel
Optionally adjust the query row limit (1-1000 rows, default is 100)
Click "Preview Data" to see your model's results
Review both the compiled SQL and data output
Download results as CSV if needed for further analysis
The Data Explorer compiles your SQL, resolves all jinja references and macros, and executes the query against your data warehouse—all without running dbt compile or building your models.
Previewing Compiled SQL
Understanding how dbt compiles your code is crucial for debugging and optimization. Click "Compiled SQL" in the Data Explorer to see exactly how your SQL, jinja syntax, and macros unfold into executable queries. This visibility helps you:
Debug complex macro logic
Optimize query performance
Understand how dbt resolves dependencies
Learn how jinja templating works in practice
Preview Specific SQL Segments
For complex models with multiple CTEs or subqueries, you can preview specific segments:
Highlight the desired SQL segment (CTE or subquery) in your file
Click the Data Explorer icon
Click "Preview Data" to see results for just that segment
This granular preview capability accelerates the development and debugging process, especially for complex transformations.
Defer to Production Feature
Paradime's defer to production functionality allows you to compile and preview models using your production state (the latest manifest.json). This is invaluable when:
Validating downstream model changes without rebuilding all upstream dependencies
Testing modifications to models deep in your DAG
Developing efficiently without waiting for full project builds
Both Preview Data and Compiled SQL actions automatically defer when this feature is enabled in your IDE settings.
Debugging and Iteration
The preview functionality transforms how you develop dbt models. Instead of the traditional cycle of write-build-check-debug, you can:
Write transformation logic
Preview results immediately on sample data
Make adjustments based on what you see
Iterate rapidly until the output matches expectations
Only then execute
dbt runto build the final model
This workflow dramatically reduces development time and creates a more interactive, feedback-rich development experience.
Creating Your First Model
With your project initialized and architecture understood, let's walk through creating your first dbt model from start to finish.
Step 1: Create a New Branch
Version control is essential for collaborative analytics engineering. Begin by creating a development branch:
Open Git Lite by clicking the source control icon in the left panel of the IDE
Using the dropdown, select + New Branch
Give it a practical, descriptive name (e.g.,
my_first_dbt_modelorfeat/customer-dimension)
Git Lite creates branches from your remote main/master branch and automatically syncs with remote branches, simplifying the branching workflow.
Step 2: Create a New File
Now you'll create the actual model file:
Click the folder icon (📁) in the left panel to view your dbt project files
Navigate to the appropriate folder (e.g.,
models/staging/for staging models)Right-click on the folder and select New File
Name your file using dbt naming conventions (e.g.,
stg_customers.sqlfor staging,dim_customers.sqlfor marts)
Consistent naming conventions are crucial for project organization. Staging models typically use the prefix stg_, intermediate models use int_, and mart models use descriptive business terms.
Step 3: Write Your dbt Model
Write SQL that transforms your data, using dbt's jinja syntax to reference sources and models dynamically:
This simple staging model demonstrates key dbt patterns:
The
config()block sets model propertiesThe
source()macro references your raw dataCTEs organize transformation steps clearly
Column renaming follows your naming standards
Step 4: Preview and Validate
Before building your model, use Data Explorer to preview your results:
With your model file open, click the Data Explorer icon
Review the compiled SQL to ensure jinja references resolved correctly
Click "Preview Data" to see sample output
Verify the transformations produce expected results
Make any necessary adjustments based on what you observe, then preview again until satisfied.
Step 5: Materialize Your dbt Model
Once your logic is validated, build the model:
Open the Terminal at the bottom of your screen
Run:
dbt run --select stg_customers(or use the "run model" dropdown in the commands panel)Review any errors or warnings that appear
Resolve issues and run again if needed
The --select flag runs only your specific model, saving time during development. Once successful, your model is materialized in your data warehouse.
Step 6: Commit and Push Your Changes
With your model built and tested, commit your work to version control:
Click the Git Lite icon in the left panel
Review your changes in the interface
Enter a commit message—or use DinoAI's "Write Commit" feature to automatically generate a detailed, meaningful commit message
Click "Commit and Push"
Git Lite automatically commits your changes, pushes to your remote branch, and pulls/merges any remote changes if needed.
Step 7: Open a Pull Request
Finally, create a pull request for team review:
Ensure all changes are committed (the "Open Pull Request" button is only enabled when there are no uncommitted changes)
Click "Open Pull Request" in Git Lite
Review your changes in your Git provider (GitHub, GitLab, etc.)
Request reviews from team members
Once approved, merge your PR into the main branch
This workflow ensures code quality through peer review and maintains a clean project history.
Best Practices and Next Steps
Model Documentation
Proper documentation ensures your dbt models are maintainable and understandable by current and future team members. Best practices include:
Describe every model: Explain what it does, why it exists, and how it should be used
Document key columns: Especially those with complex business logic or domain-specific meanings
Use doc blocks: For longer explanations that can be reused across multiple models
Keep documentation close to code: Store YAML files alongside the models they document
Well-documented models reduce onboarding time, prevent errors, and create institutional knowledge that persists beyond individual contributors.
Testing Strategy
Implement a comprehensive testing strategy that maintains data quality throughout your pipeline:
Test all primary keys for uniqueness and not-null constraints
Validate relationships between models using referential integrity tests
Add accepted_values tests for categorical columns with known domains
Create custom tests for business-specific logic and constraints
Run tests in CI/CD to catch issues before they reach production
Tests act as guardrails that catch data quality issues early, when they're easiest and cheapest to fix.
Deployment and Scheduling
Once your models are built and tested, deploy them to production using Paradime Bolt's orchestration capabilities:
Schedule regular runs aligned with your data refresh requirements
Set up alerting for failed runs or data quality test failures
Monitor performance using Paradime Radar's column-level lineage and observability features
Implement incremental models for large datasets to improve efficiency
Production deployment transforms your development work into reliable, automated data pipelines that power business intelligence and analytics.
Conclusion
Building your first dbt model in Paradime is a streamlined process that combines the power of dbt with an intuitive, AI-enhanced development environment. By following this guide, you've learned to initialize projects, structure models using proven layering strategies, leverage preview functionality for rapid iteration, and use Git workflows for collaborative development.
The combination of Paradime's integrated tooling—DinoAI for intelligent assistance, Data Explorer for instant preview, and Git Lite for simplified version control—creates a development experience that's both powerful and accessible. As you continue building models, these foundational patterns will scale to support sophisticated analytics engineering projects.
Remember: start simple, test thoroughly, document comprehensively, and iterate based on feedback. With Paradime's AI-powered workspace and dbt's transformation framework, you have everything needed to build production-grade analytics pipelines that drive data-informed decision-making across your organization.